The different chemical products
CLASSIFICATION OF TOXIC CHEMICALS
Toxic chemicals include organic solvents, reactive chemicals and pure (or diluted) compounds that have adverse health effects.
The effects of toxic chemicals may be of two kinds:
- Acute toxicity: in the case of high exposure, leading to short-term effects: illness, death
- Chronic toxicity: repeated exposure to a substance may cause long-term effects: degenerative illness, cancer, reprotoxicity, neurotoxicity. Compounds with chronic toxicity include the so-called CMR products (Carcinogenic, Mutagenic, Reprotoxic)

Hydroxymethylfurfural
Products that may pose a danger to human health are labelled with four pictograms (listed in the table of hazard pictograms):
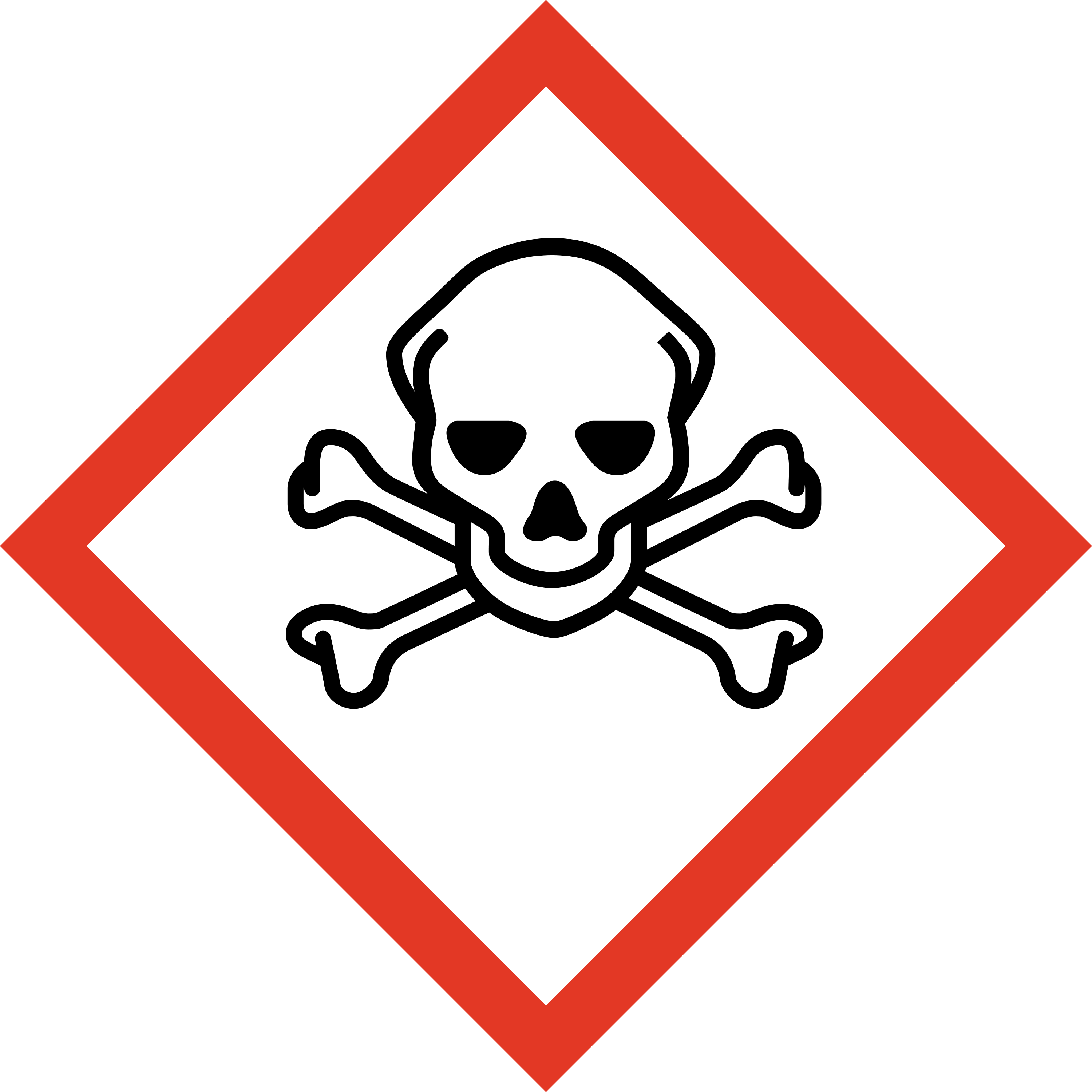

Toxic substances:
category 1,2,3
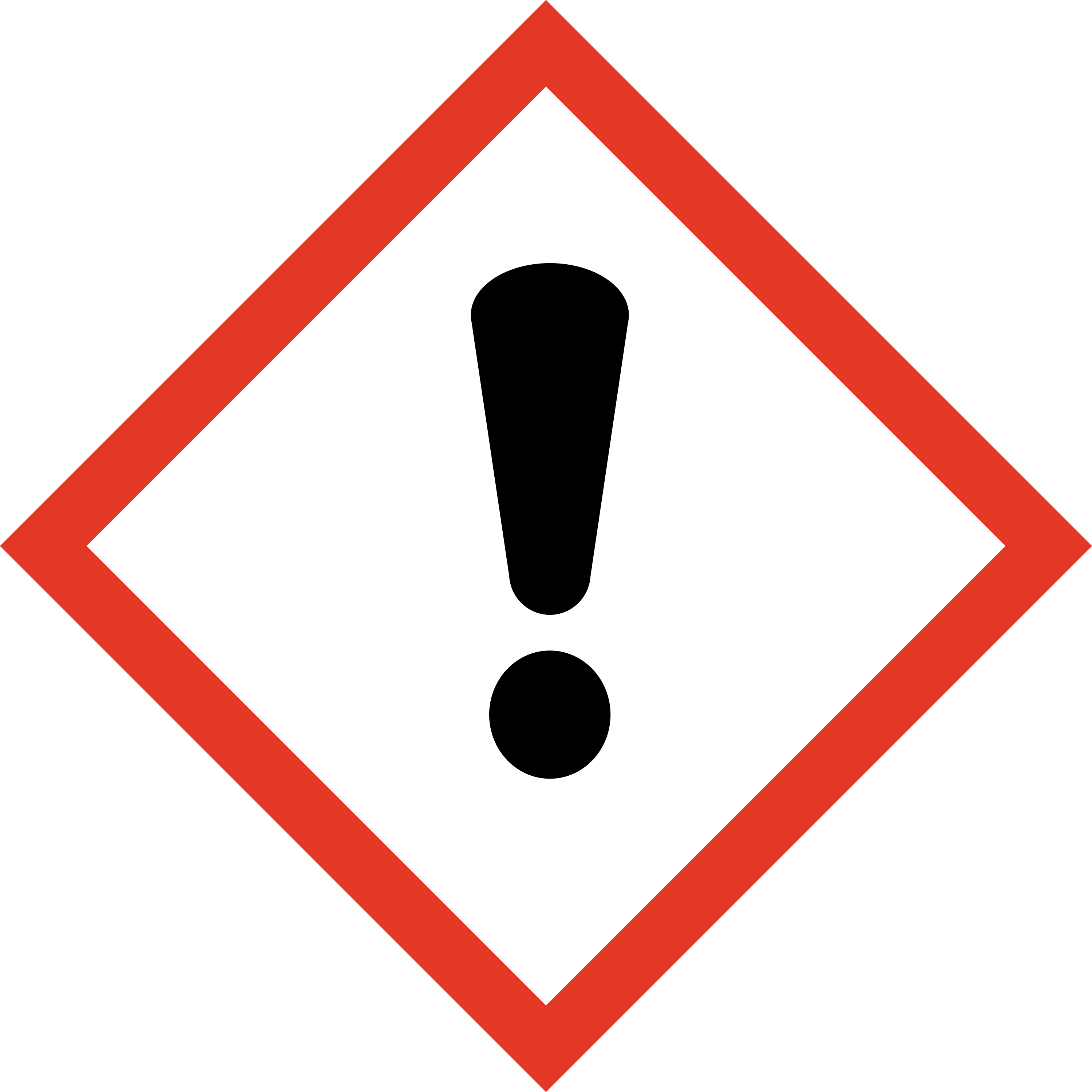

Toxic substances:
category 4
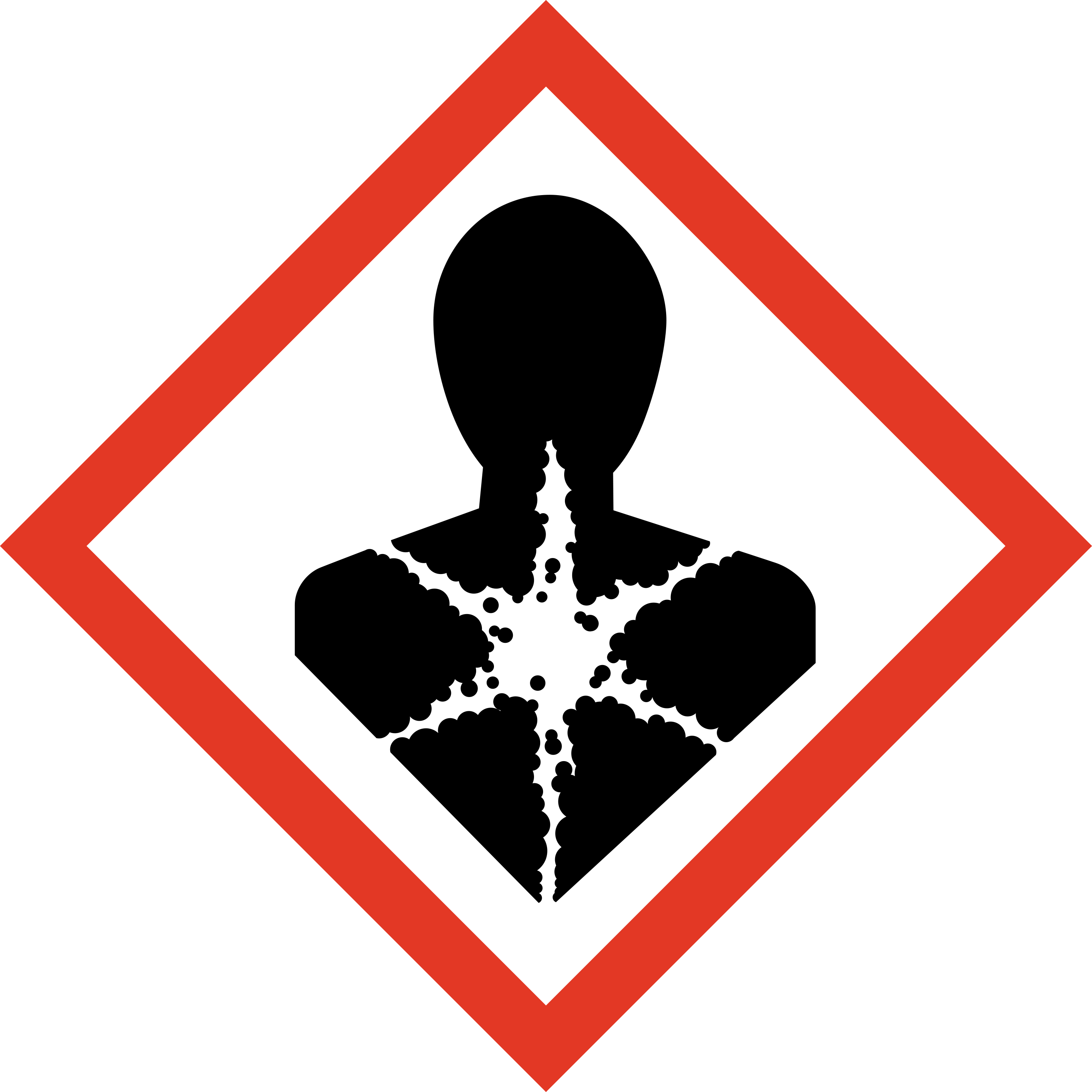

Substances with a particular toxicity
Corrosive substances
The pictograms alone are not sufficient to characterize a hazard. The CLP regulation requires the addition of hazard statements which more precisely specify the potential dangers of a chemical product, such as: “H300: Fatal if swallowed”. The label of a bottle of methanol can be seen below, displaying various hazard statements.
HAZARD STATEMENTS RELATED TO HEALTH
H300 Fatal if swallowed
H301 Toxic if swallowed
H302 Harmful if swallowed
H304 May be fatal if swallowed and enters airways
H310 Fatal in contact with skin
H311 Toxic in contact with skin
H312 Harmful in contact with skin
H314 Causes severe skin burns and eye damage
H315 Causes skin irritation
H317 May cause an allergic skin reaction
H318 Causes serious eye damage
H319 Causes serious eye irritation
H330 Fatal if inhaled
H331 Toxic if inhaled
H332 Harmful if inhaled
H334 May cause allergy or asthma symptoms or breathing difficulties if inhaled
H335 May cause respiratory irritation
H336 May cause drowsiness or dizziness
H340 May cause genetic defects
H341 Suspected of causing genetic defects
H350 May cause cancer
H351 Suspected of causing cancer
H360 May damage fertility or the unborn child
H361 Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child
H362 May cause harm to breast-fed children
H370 Causes damage to organs
H371 May cause damage to organs
H372 Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure
H373 May cause damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure

Instructions for handling
More than any other chemicals, toxic chemicals must be handled with care. A few guidelines should also be followed to reduce the risk when handling these compounds:
- Wear personal protective equipment and handle only under a fume hood with the sash properly lowered ;
- Keep the lab bench clean to avoid accidents and product spills ;
- The bottle of a toxic product should be left open for the briefest time possible. Do not open it until just before you are about to handle the product, and close it again immediately afterwards;
- Never leave bottles of toxic chemicals at the front of the lab bench. After use, move them to the back of the bench to avoid knocking them over ;
- Always focus on one step at a time. Never try to carry out several steps of an experiment at the same time.




