Basics of GC
The injector’s role
- To introduce into the chromatograph a precise volume of sample for analysis without disturbing the flow of the gaseous mobile phase in the system.
- For non-volatile samples at room temperature, to vaporize them so that they are transported towards the separation column by the carrier gas.

The injector’s role
- To vaporize the sample.
- To introduce the volatile compounds into the separation column.
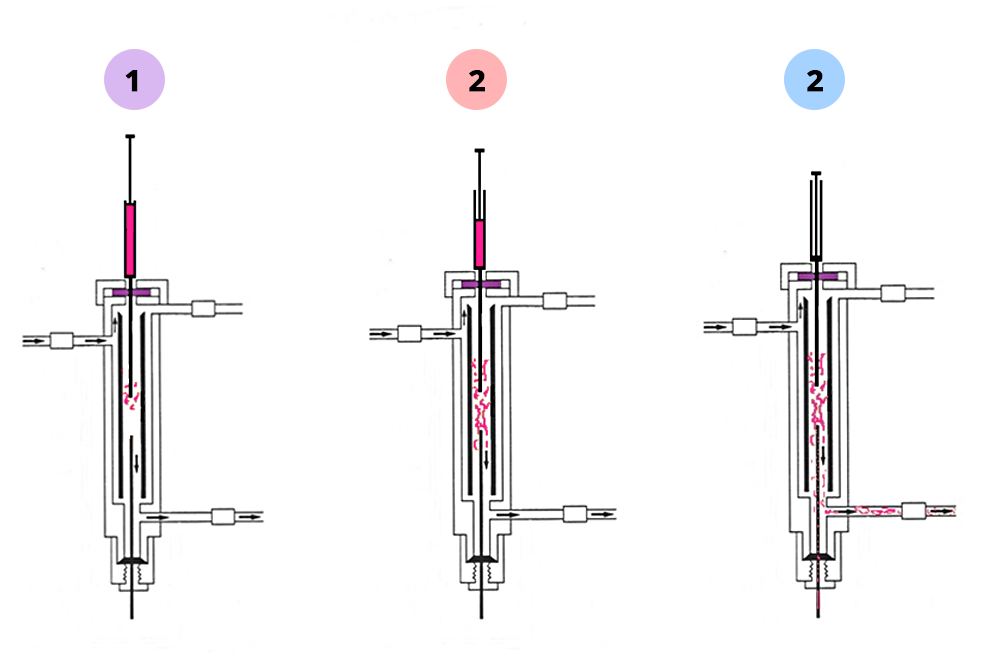
The injector’s role
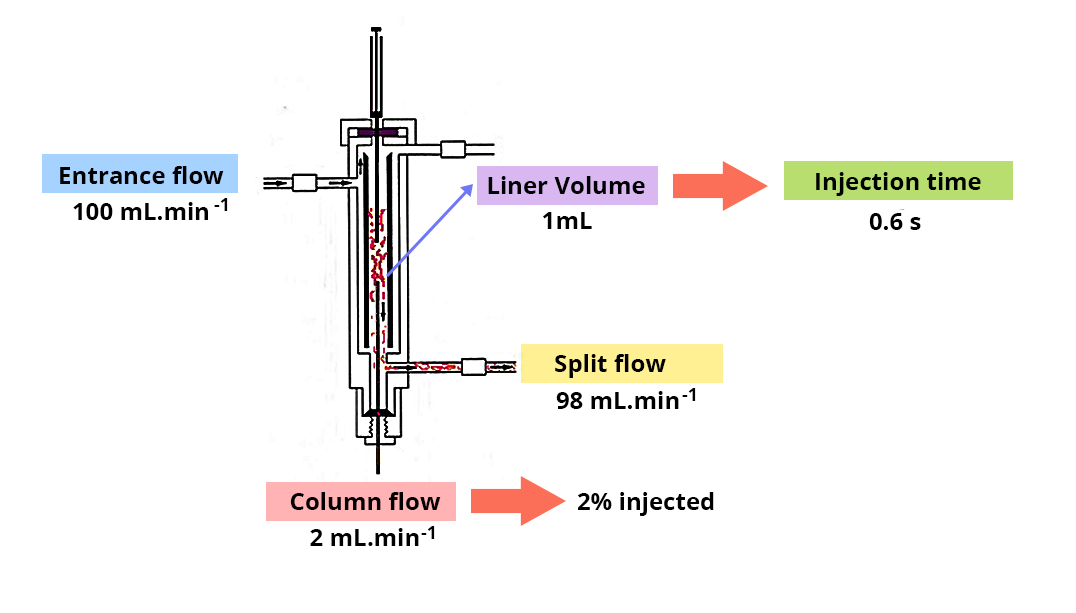
- To prevent the distortion of chromatographic peaks by rapid injection and non-saturation of the stationary phase: division mode (split).
The injector’s role
- Very diluted sample in a solvent, no risk of column overloading: without division (splitless mode)
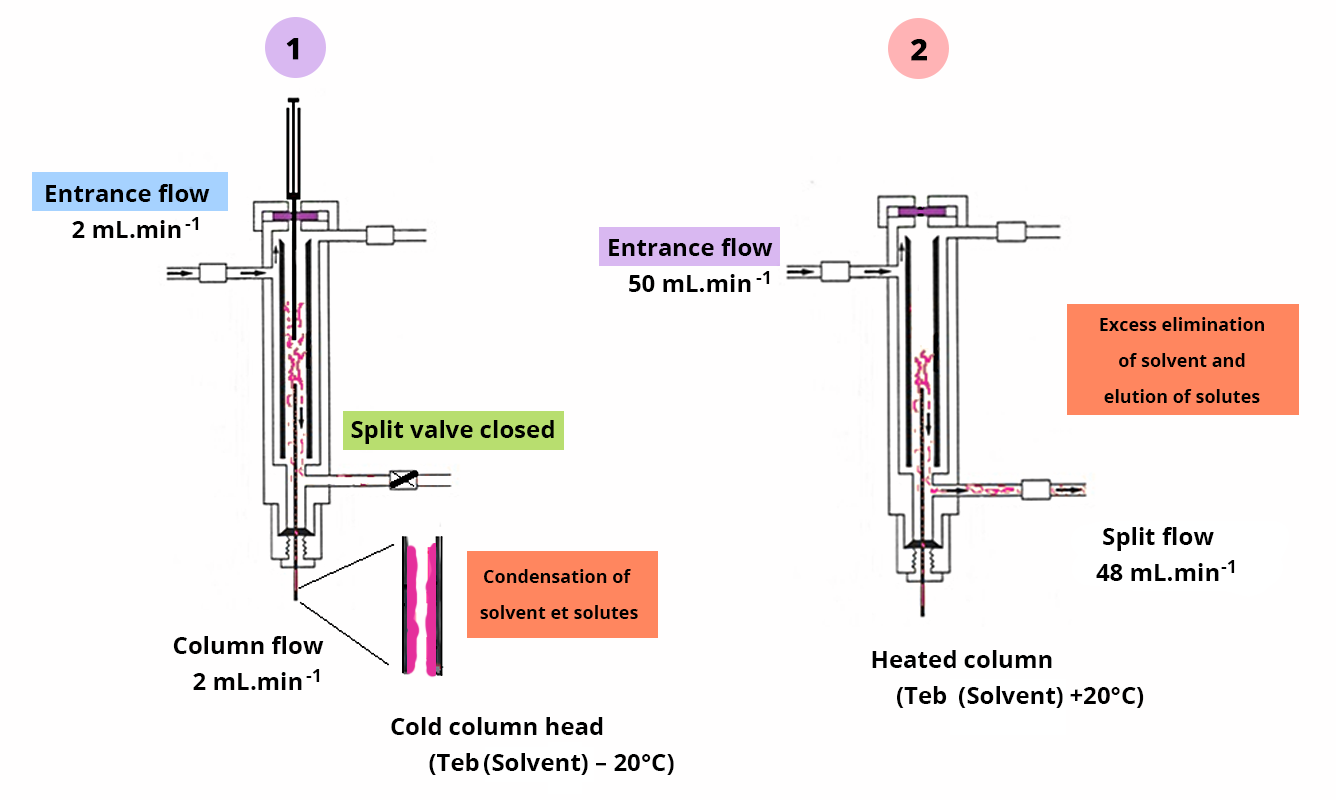
- Splitless mode in two stages:
- Transfer of the sample to the column head with condensation of solvent
- Solvent vaporization and initiation of analyte elution
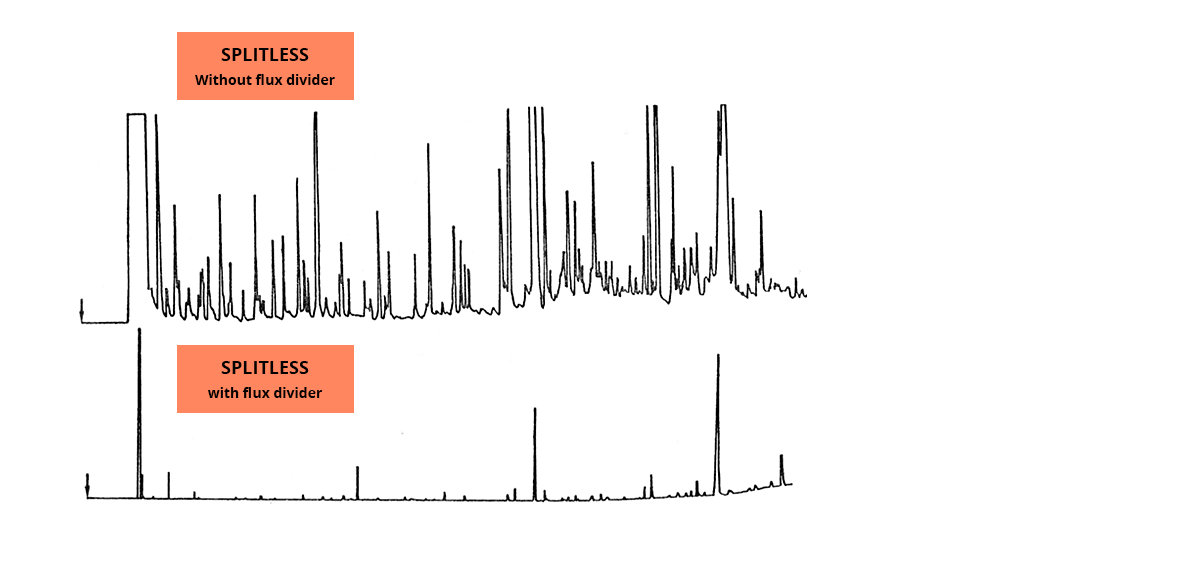
Split/splitless injection?
Adapting the injection type to the sample, especially taking into account its concentration.