Potentiometric titration of base salts
HOW TO DETERMINE THE ACTIVE INGREDIENT CONTENT IN A DRUG BY POTENTIOMETRIC TITRATION
This method is largely used in drug control.
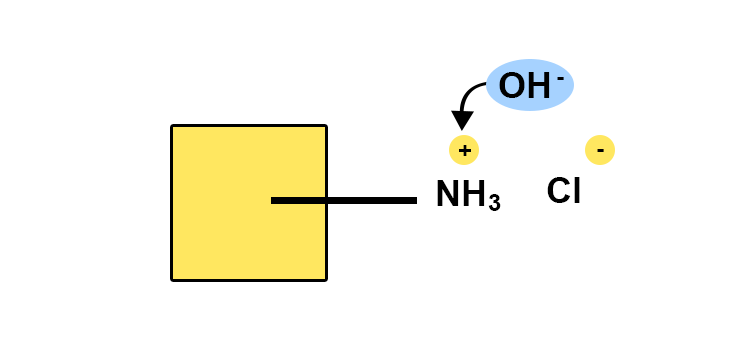
- The assay discussed here is the potentiometric titration of lidocaine hydrochloride, which is a halogenated salt of an organic base. This assay is also known as the Billon method.
- This titration method has the advantage of being specific to the organic part, as it is the protonated base BH+ (i.e. the conjugated acid) that is being titrated. This is done in ethanol because, in this solvent, most of the protonated bases are acids strong enough to be determined by sodium hydroxide. Potentiometric detection reveals the equivalence point. The volume of sodium hydroxide is used to calculate the titration in BH+ and therefore in the corresponding base.