Analysis of a spring water
Determination of NO3- ions with a selective electrode (potentiometry)
How it works
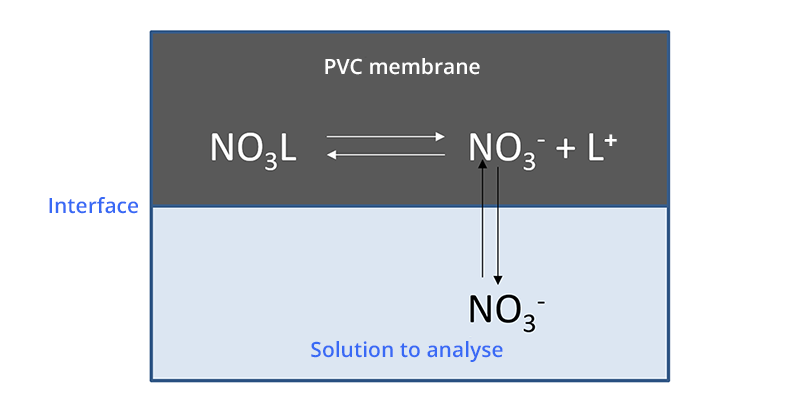
The operating principle is similar to that of the calcium ion selective electrode.
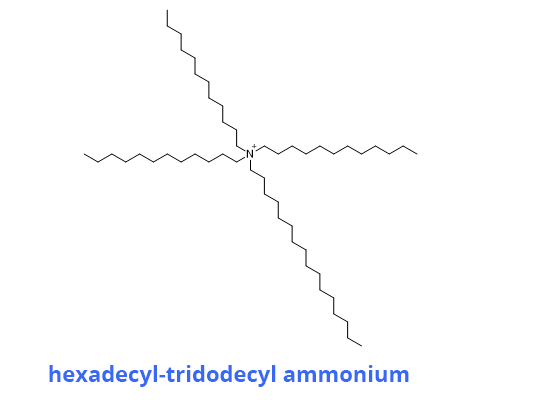
The membrane of the electrode contains a reagent that complexes NO3- ions (ionophore) almost selectively. This is often hexadecyl-tridodecyl ammonium nitrate.
When the membrane comes into contact with an aqueous solution containing NO3- ions, this results in a potential difference at the membrane-solution interface.