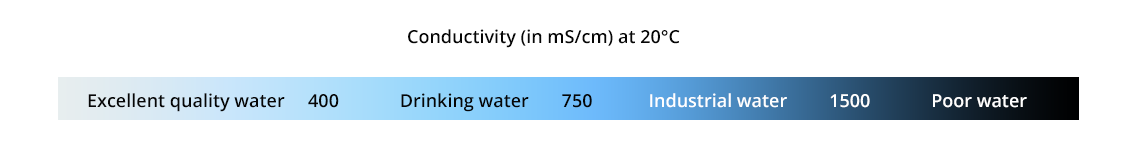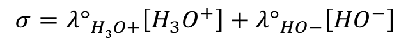A conductivity meter is a device for measuring the conductivity σ (expressed in S.m-1) or the resistivity ρ (expressed in Ω.m) of a solution.
In practice, the device measures a conductance G (expressed in Siemens Ω-1) or a resistance R (expressed in Ω) (R = 1/G).
The property of electrical conductance (or resistance) relates to the movement of ions (ion mobility ui).
Why measure conductivity?
- To follow up a titration in addition to potentiometric, pH-metric or colorimetric monitoring (acetic titration in vinegar, basicity of Destop®) or to determine the concentration of ions in solution (Cl- in milk, SO42- in mineral water).
- To check the quality of water: the conductivity of ultrapure water is about 0.055 mS/cm at 25°C.
- To determine kinetic constants or thermodynamic constants (pKA, pKS, E°).