What is the aim of the experiment?
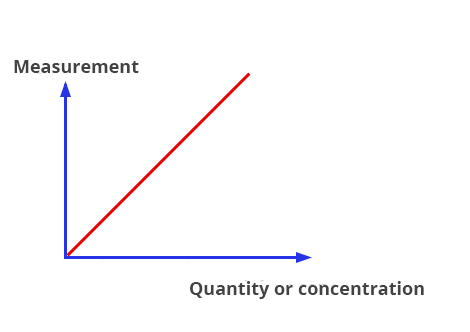
To establish the existing relationship between the measurement result and the quantity (or concentration).
Several types of calibration according to the measurement method: external, internal, standard additions. This sheet will present external calibration in further detail.
Several types of calibration according to the measurement method: external, internal, standard additions. This sheet will present external calibration in further detail.
What is its purpose?
To estimate the amount (or concentration) of a target compound (molecule/ion/atom) in a sample.


Practical constraints
Having a standard available (target compound in the case of external calibration or standard additions, similar compound if internal calibration).
Having access to the measuring device (spectrophotometer, HPLC-UV, or other depending on the intended analysis).
Stay within the linear range of the instrument, if possible.
Having access to the measuring device (spectrophotometer, HPLC-UV, or other depending on the intended analysis).
Stay within the linear range of the instrument, if possible.




