Basics of NMR
First order or second order spectra
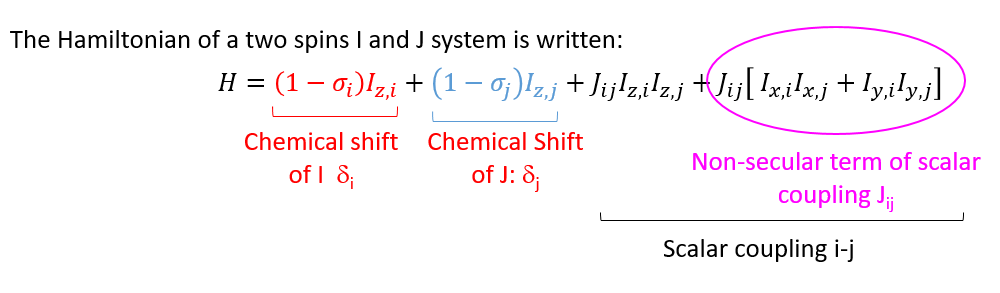
When the non-secular term has a negligible contribution compared to secular terms, the spin system is of the first order: The rules of multiplicity of Pascal's binomial apply in this case only.
- In order to detect whether a signal is of the first or second order, the following quantity must be evaluated:

- Approximation of weakly coupled nuclei: :

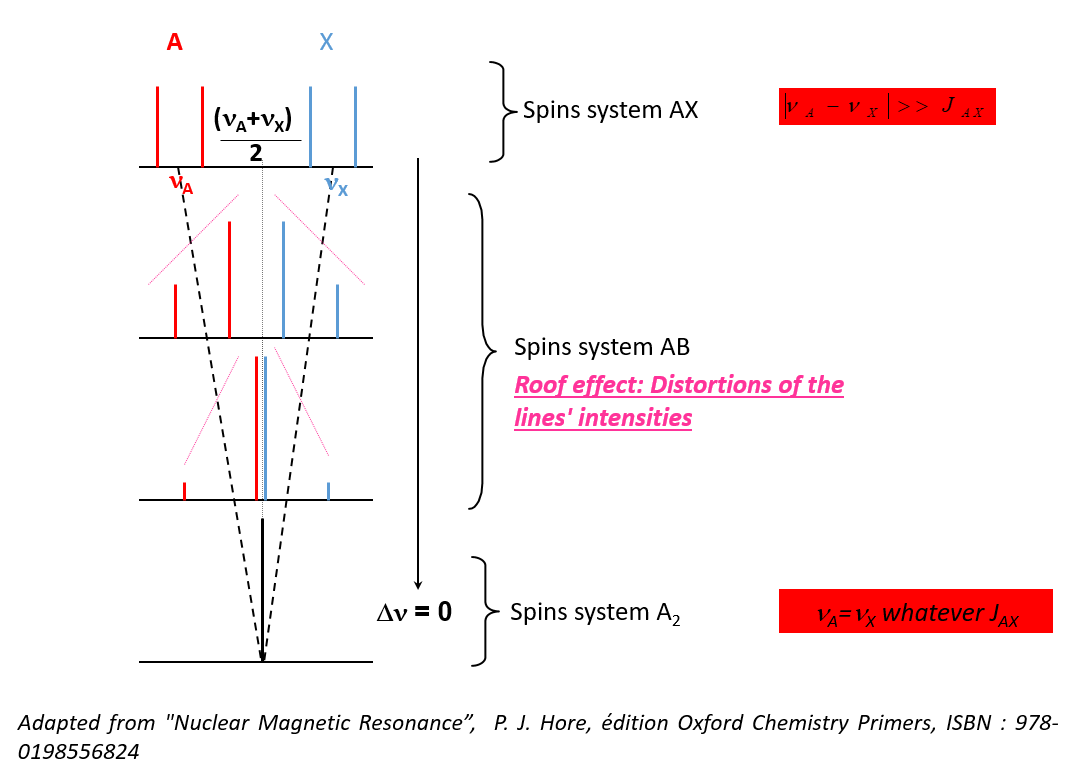
I and J are then written A and X, the spectrum is of the first order - If this condition is not respected, the nuclei are said to be strongly coupled

- Changes in the intensity of the lines
- Changes in the number of lines
- Spectral analysis requires theoretical calculations
Spectral analysis requires the simulation of NMR spectra
Consequences:- It is no longer possible to measure J directly (except in the simple case AB)
- Source of error in the interpretation of the spectra
- Spectra analysis request calculation
-
Analyze the sample with a higher magnetic field
- Δν depends on B0
J is independent of B0
- Approximation of weakly coupled nuclei: :
Isochrony
-
Two nuclei are CHEMICALLY EQUIVALENT, if they have the same chemical environment, that is if geometrically there is at least one element of symmetry (plane, axis, center) between them.
- If the symmetry element is at least one proper axis of symmetry, the nuclei are said to be homotopic
- If the symmetry element is strictly an improper axis of symmetry (center, plane, axis of rotation-reflection), the nuclei are called enantiotopes
The two nuclei therefore have the same NMR resonance frequency: they are ISOCHRONES
Isogamy
- Two nuclei are ISOGAMIC if they have the same coupling relationships with any of their neighbors that do not have the same chemical shift.
Remarks:- Two nuclei cannot be isogamic if they are not at least isochronous
- It makes no sense to test the isogamy of a pair of nuclei if they do not have at least the same chemical environment. Indeed, in this case, they necessarily already have different coupling relationships with a given third party!
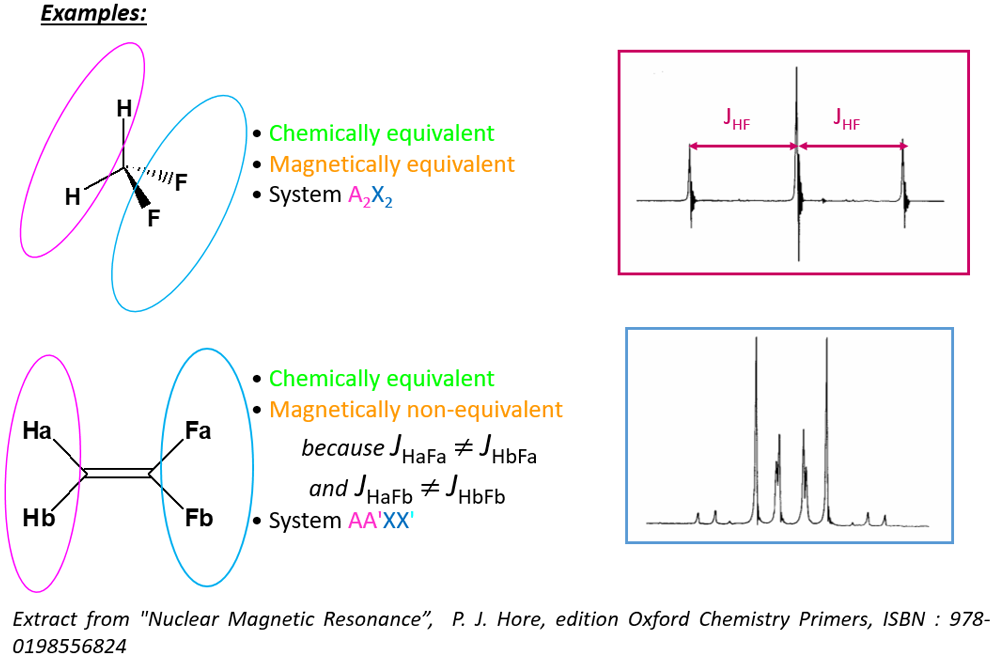
Chemical and magnetic equivalence
- Two CHEMICALLY EQUIVALENT nuclei are ISOCHRONOUS
- Two MAGNETICALLY EQUIVALENT nuclei are ISOCHRONOUS & ISOGAMIC
Corollaries:- Two nuclei can therefore be chemically, but not magnetically, equivalent if they are not isogamic.
- Two magnetically equivalent nuclei are necessarily chemically equivalent
Nomenclature of spin systems
- Nuclei that have no equivalence relations are written with different letters
Example: AX, AMX… - Magnetically equivalent nuclei or clusters of nuclei are written with the same letter, indicated by the number of nuclei involved in each group
Example: A2, X2, X6, A3X2, AMX2, ... - Chemically equivalent nuclei or clusters of nuclei are written with the same letter, but are differentiated from each other by a typographic character. There are as many characters as there are spins involved in the group considered
Example: AA’, XX’, AA’KX3, AA’A ’’A’’’A(4)A(5)A(6)...