Adsorption Titration
An indicator is added to the solution and can be adsorbed on the surface of a colloidal suspension containing the analyte SEint(s).
This technique relies on the difference in surface charges of the particles before and after the equivalence point.
Before the equivalence point, the Ind- indicator is free in solution, with the same charge as the surface charge of the particles. Thus it is repelled by the particles (electrostatic interaction) and colors the solution.

After the equivalence point, the surface charge is reversed. The indicator is adsorbed on the surface of the particles where it forms a precipitate of a different color from that of the free indicator in the solution.

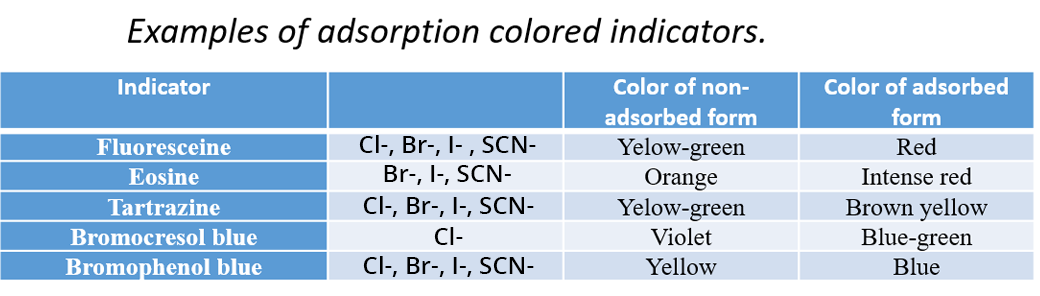
This technique is used in particular for the titration of halide ions: I-, Br- and Cl-. n this case, the titrant is the Ag+ ion. As soon as Ag+ is added, a colloidal precipitate of AgI, AgBr or AgCl is formed.







