Henry's law constant
Henry's law constant reflects the volatility of a solute in aqueous solution.
It represents, at equilibrium, the partition coefficient of the solute between the aqueous solution and the gas phase:

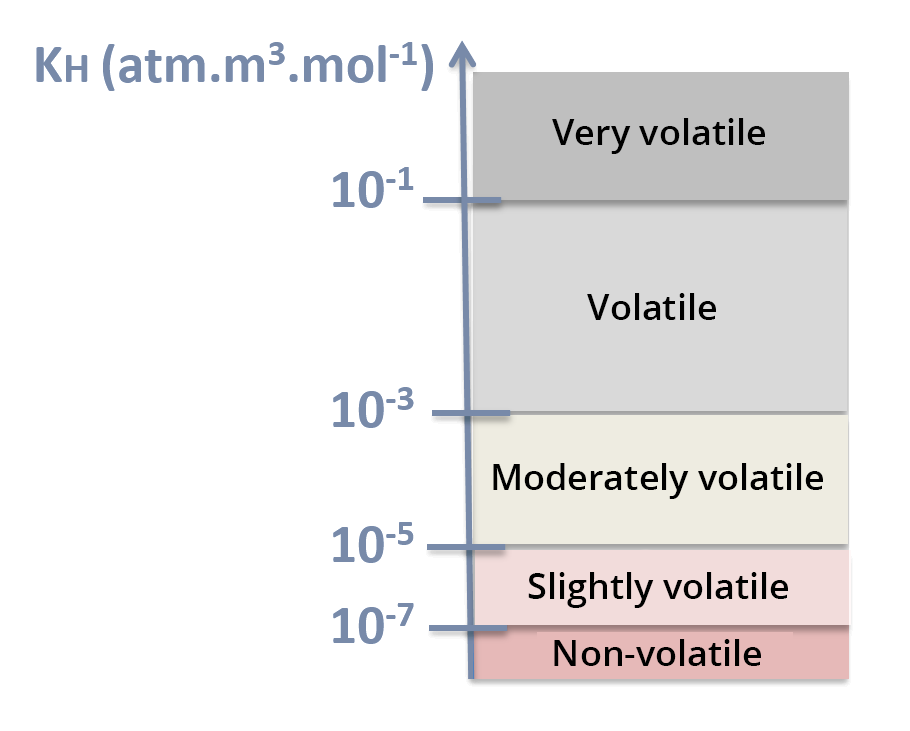
Henry's law constant is expressed in atm.m3.mol-1. The higher Henry's law constant, the more volatile the compound is – see KH scale.
In the case of a dilute aqueous solution, Henry's law constant can be easily estimated from the values of the compound’s water solubility and vapor pressure: