Contaminant analysis in complex matrices
Contaminant
Any a priori investigation of a contaminant must take into account its chemical structure and its physicochemical properties in order to choose the most appropriate analytical method. Knowing the stability of the molecule is also useful in order to take the necessary measures to avoid its degradation.
When no specific contaminant is initially targeted, several analytical methods should be implemented in order to be able to analyze more or less hydrophobic or more or less volatile contaminants.
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE?
The chemical structure of the molecule (cf. its structural formula) and the presence of certain groups (e.g. alcoholic, amino or carboxylic acid functions, aromatic rings) are useful in anticipating the molecular interactions that the contaminant is likely to develop (in the sample and with the solvent too). The chemical structure helps to guide your choice of extraction conditions and the potential pre-treatment of the matrix.
STABILITY?
It is also useful to know the stability of the contaminant of interest, especially its sensitivity to hydrolysis, oxidation, photolysis or temperature. Thus, you can choose analytical conditions that will preserve the molecule. Sometimes, modifying the sample (e.g. pH adjustment, the addition of stabilizer) can prevent degradation of the contaminant.
When a molecule turns out to be very unstable, the analysis must be performed very quickly and you will have to look for the known degradation product(s) of the initial contaminant.


Your Investigation
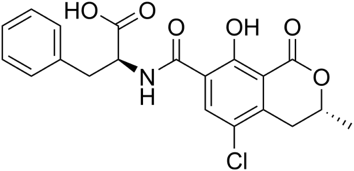
The structure of ochratoxin A is presented below. Its pKa is 7.1. Its solubility in water is about 1mg/L at 25°C. The molecule is very stable. Suggest an extractant for this contaminant.
Clue
The molecule is slightly soluble in water. An organic solvent like methanol can be used (hydrogen bonding interactions are possible).