Exercise 3: Use of an internal standard
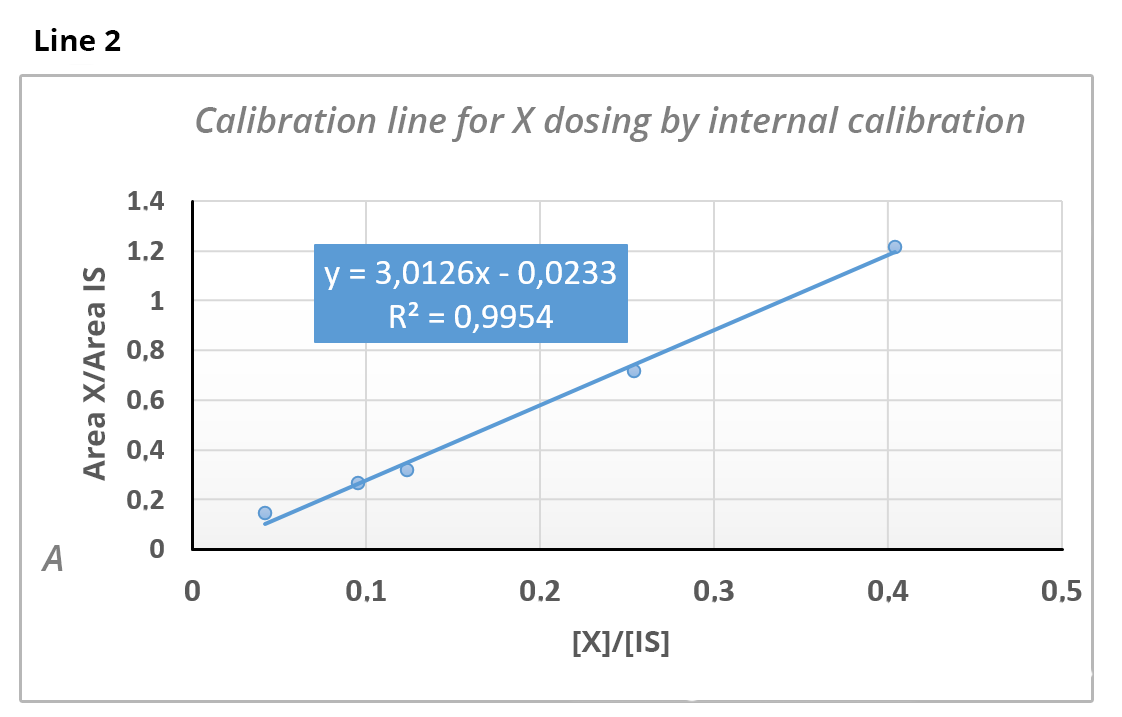
The dosage of substance X is carried out by standard additions in the presence of an internal standard (IS) (line 1) and by internal calibration in the presence of the same IS (line 2).
The ratio of the areas obtained for the sample solution is: Areasample / AreaIS = 0.340
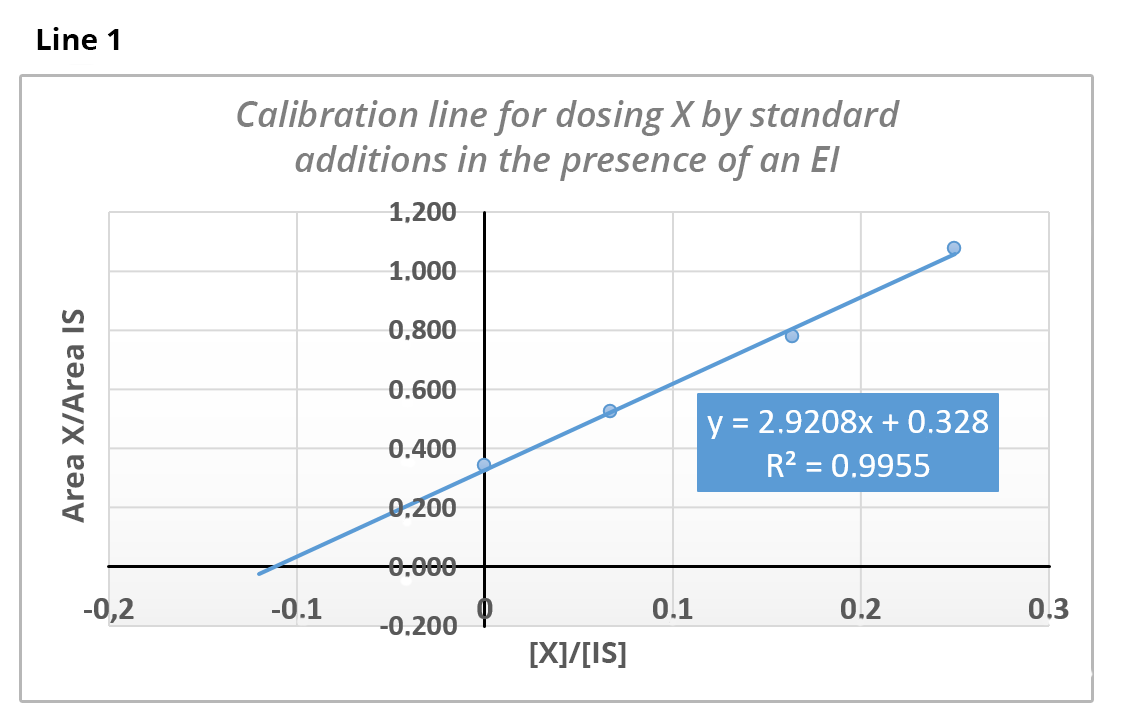
Knowing that the concentration of the IS is 79 ppm, calculate from line 1 the concentration of X in the analyzed solution.
[X] = 25.9 ppm
[X] = 10.18 ppm
[X] = 8.87 ppm As quantification is carried out by standard additions, we have y = 0 => x = -0.328/2.92 = 0.112 =>
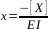 then[X] = 0.112 x 79 = 8.87 ppm.
then[X] = 0.112 x 79 = 8.87 ppm.Knowing that the concentration of the IS is 75 ppm, calculate from line 2 the concentration of X in the analyzed solution.
[X] = 7.92 ppm
[X] = 26.02 ppm
[X] = 9.04 ppm As quantification is performed by internal calibration and y = 0.34 => we have x = (0.34 + 0.0233)/3.0126 and
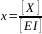 => [X] = 9.04 ppm
=> [X] = 9.04 ppm



