Hydrophobic interaction
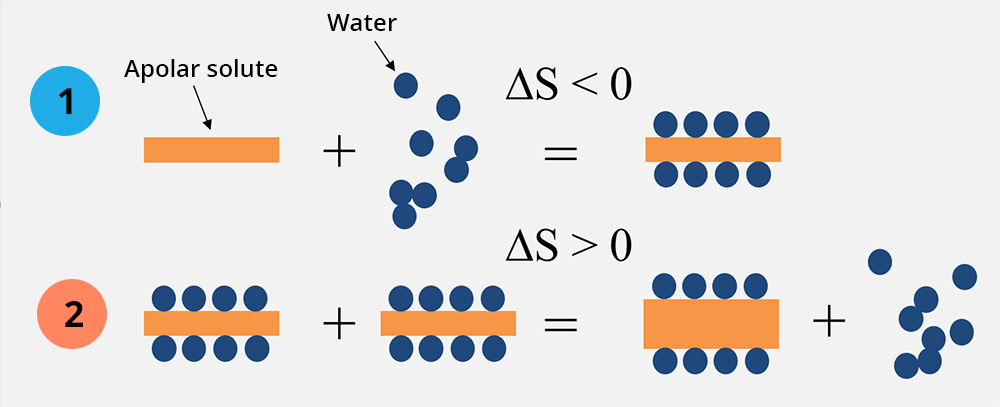
Hydrophobic interaction involves apolar molecules in aqueous solutions. It is an entropic process, which occurs spontaneously in 2 stages:
Stage 1: the apolar solute is solubilized by water molecules – as a result, the order of water molecules in the medium increases, which decreases the entropy (loss of entropy: unfavorable process).
Stage 2: two solvated molecules of apolar solute interact (hydrophobic interaction), leading to a reorganization of the water molecules around them to solvate them – as a result, water molecules are released into the medium, which increases disorder (gain of entropy – favorable process).
As the entropy gain linked to the hydrophobic interaction is greater than the entropy loss in stage 1, the process occurs spontaneously in an aqueous medium.